Science in medicine
Introduction:
'Science is the
father of knowledge, but opinion breeds ignorance', opined the Hippocratic
treatise The Canon, and Hippocratic practitioners developed an approach to
health, disease, and its treatment based on systematic observation and
cumulative experience. Even the word physic, the root of physician as well as
physicist, derives from the Greek for 'nature'. Further, Hippocratic medicine
was experimental, that word stemming from the same classical roots which gave
us 'experience'.
Bringing the best evidence to the point of care
Definition:
'Evidence-based
medicine is the conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current best
evidence in making decisions about the care of individual patients. This
practice means integrating individual clinical experience with the best
external clinical evidence from systematic research'.
History:
With basic research
continually developing new diagnostic and treatment modalities. The methods for
conducting and the criteria for assessing, research have been considerably
strengthened in the twentieth century. Bradford Hill introduced the randomized
trial to medicine: the Medical Research Council trial of streptomycin for
pulmonary tuberculosis in 1948. Since then more than a quarter of a million
such trials have been conducted. Almost simultaneously, Yerushalmy introduced
greater rigour into the evaluation of diagnostic tests by quantifying the
accuracy the sensitivity and specificity of chest radiograph screening for
pulmonary tuberculosis.

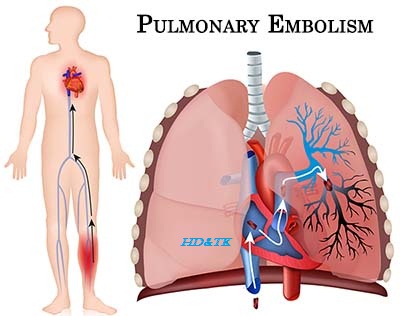

Comments
Post a Comment